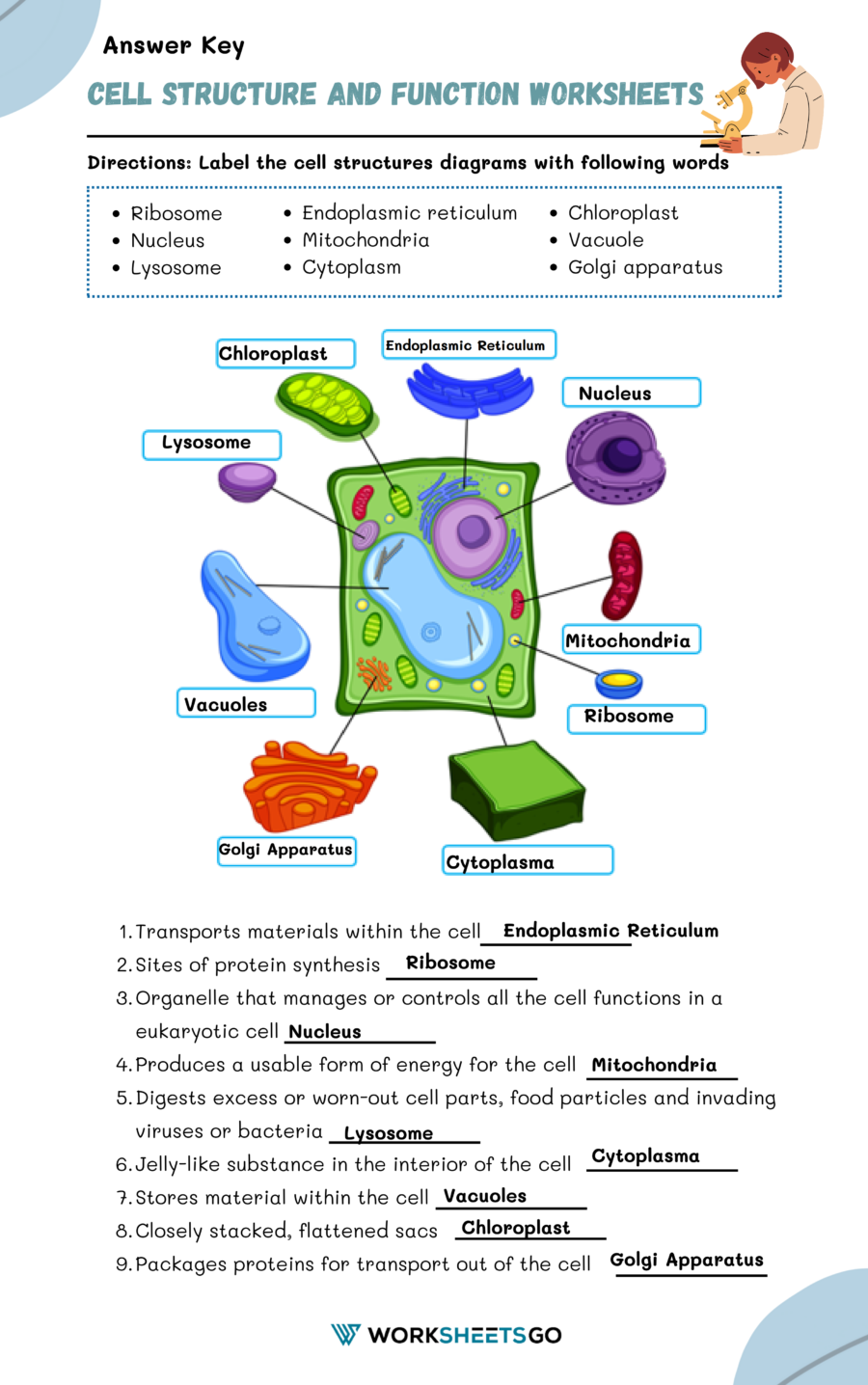
Cells are often referred to as the “building blocks of life” because they are the smallest units that can perform all of the necessary functions for life. All living organisms, from the tiniest bacteria to the largest whales, are made up of cells. Some organisms, like bacteria, are unicellular (consisting of a single cell), while others, like humans, are multicellular (consisting of many cells).
Key Cell Structures and Their Functions
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane):
- Structure: A thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell.
- Function: Regulates what enters and leaves the cell; provides protection and support.
- Cytoplasm:
- Structure: Gel-like fluid inside the cell.
- Function: Houses the cell’s organelles and is the site of many cellular processes.
- Nucleus:
- Structure: Large, spherical structure usually located near the center of the cell.
- Function: Controls all cell activities; contains the cell’s DNA.
- Mitochondria:
- Structure: Bean-shaped with a double membrane.
- Function: Produces energy (ATP) for the cell through cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):
- Structure: Network of tubules and sacs.
- Function: Synthesizes and transports proteins and lipids.
- Golgi Apparatus:
- Structure: Stack of flattened sacs.
- Function: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport.
- Lysosomes:
- Structure: Small, spherical organelles.
- Function: Break down waste materials and cellular debris.
- Vacuoles:
- Structure: Large, sac-like structures.
- Function: Store materials like water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Worksheet Activity
Now, let’s put your knowledge to the test with a worksheet activity!
Directions: Label the cell structures diagrams with following words.
| Cell Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Produces energy for the cell |
| Cytoplasm | Regulates what enters and leaves the cell |
| Nucleus | Breaks down waste materials |
| Mitochondria | Houses the cell’s organelles |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Controls all cell activities |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies and packages proteins |
| Lysosomes | Synthesizes and transports proteins and lipids |
| Vacuoles | Stores materials like water and nutrients |
I hope this gives you a clear understanding of the basic cell structures and their functions. Remember, cells are incredibly intricate, and there’s a lot more to explore in this topic. If you have any questions, feel free to ask!

Answer Key