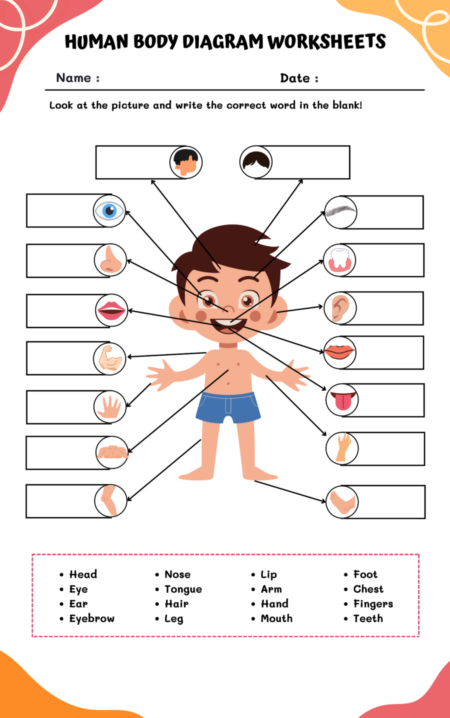
If you choose to drink alcohol, low-level drinking is less risky than heavy drinking or binge drinking. There is no level of safe alcohol consumption. A few seconds after your first sip, alcohol starts to change how your body works. After years of heavy drinking, those changes add up. Alcohol is a powerful chemical that can have a wide range of adverse effects on almost every part of your body. Alcohol affects everyone. How it affects you depends on how much you drink, your health, your age, and other factors. Drinking too much can lead to harmful short-term and long-term effects. It can affect your physical and mental health, your job, your finances, your family, and your community.
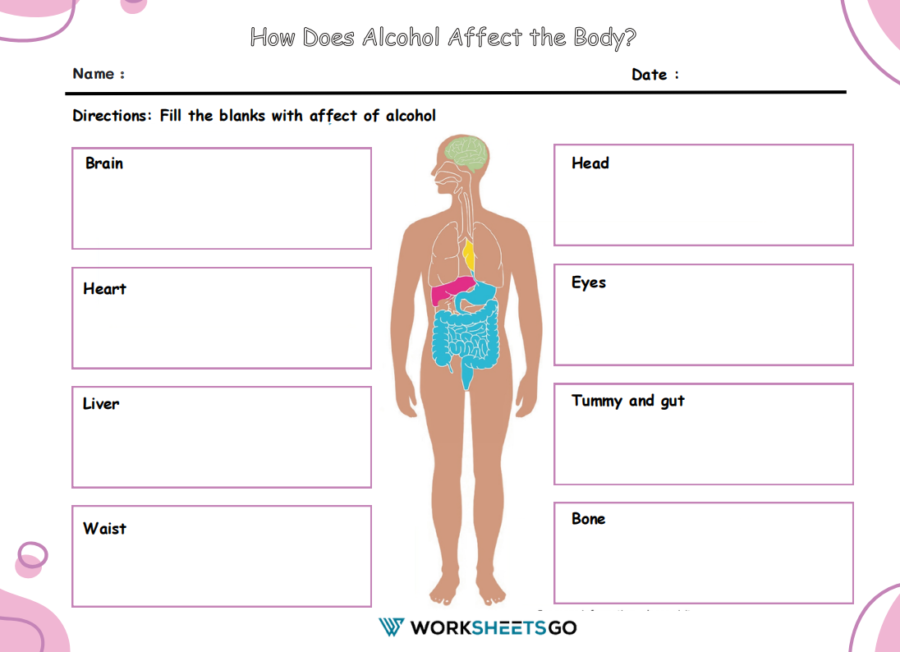
This worksheet is to improve students’ science skills about how alcohol affects the body. In this worksheet, students are asked to state the effects of alcohol on each organ of the body. These worksheets can be used as study materials for a test or quiz student.
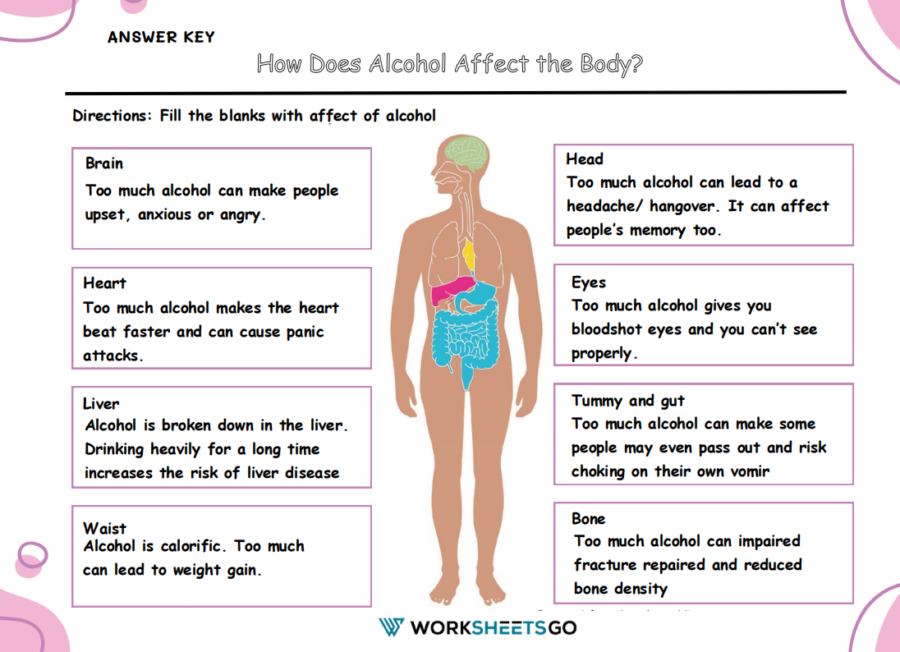
The worksheet is typically structured with a diagram of the human body, with blank spaces next to each major organ or system affected by alcohol. Here are some insights that could be filled in the blanks, highlighting the detrimental effects of alcohol:
Brain: Alcohol can interfere with the brain’s communication pathways, affecting mood and behavior, and making coordination more difficult, which may lead to the risk of accidents and injuries.
Heart: Heavy drinking takes a toll on the heart, potentially causing high blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, or an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Liver: One of the most known effects of alcohol is liver damage, which can lead to fatty liver, hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
Waist: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to weight gain due to its high-calorie content, contributing to obesity and related health issues.
Head: Alcohol can cause headaches and migraines, and chronic consumption might lead to persistent head pain.
Eyes: Vision can be impaired by alcohol consumption, leading to blurred or double vision and even long-term damage to the optic nerve.
Tummy and gut: Alcohol irritates the digestive system and can cause issues such as acid reflux, gastritis, and in the long term, might contribute to the development of stomach ulcers.
Bone: Drinking heavily can lead to thinning bones (osteoporosis), increasing the risk of fractures.
Incorporating these worksheets into educational sessions can lead to more informed discussions about health. They also provide a tangible way for learners to visualize and understand the consequences of alcohol consumption. When used effectively, such worksheets not only educate but also encourage individuals to make healthier lifestyle choices.
Answer Key
Remember, the goal of these resources is not to scare, but to educate and provide a clear picture of the choices and their effects on the human body. It’s important to use these worksheets as a starting point for deeper discussion about the role of alcohol in one’s life and society.